|
Asbestos is defined by Webster as: |
|
|
|
„Inextinguishable; grayish
mineral; a silicate of calcium and magnesium, which occurs in long, threadlike
fibers. It is incombustible and a nonconductor of electricity, used as
fireproofing material for buildings, safes, for roofing and flooring
material, for packing, steam joints and pistons.“ |
|
|
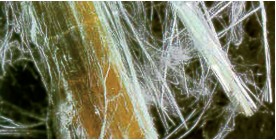
| This actually means that
asbestos is a naturally occurring mineral
fiber with high tensile strength. Asbestos fibers can be woven and
are resistant to many chemicals and to fire. Asbestos is a fibrous
form of mineral silicates belonging to the serpentine and amphibole groups of
rock forming minerals. The widely used asbestos types are, for
example: |
| |
| Chrysotile (white
asbestos) a product of serpentine rock, its fibers are curled,
which isn’t the case in the other types.
Amosite (brown/or grey asbestos) with
straight, brittle fibers, found in large quantities in South Africa.
Crocidolite (blue asbestos), a part
of the amphibole group, mostly made of sodium iron magnesium silicate.
Actinolite derives out of metamorphic rocks (it is
of hard fibers, less likely to be inhaled than the soft fibers) is the least
exploited form of asbestos, utilized sometimes for jewelry.
Anthophyllite is really chains of crystals, created
during the breakdown of the mineral talc. It can be in various colors, can be
found in sealants and paints.
Then there are other forms of amphilbole asbestos which are
tremolite (mostly white asbestos) used in talcum powder, as
well as in home and garden products. |
| |
| Asbestos has been
used for centuries around the world. Due to the variety of positive attributes
and its inexpensive application, it has been used during the last 100 years for
a wide range of manufactured goods, fire retardant coatings, concrete, bricks,
pipes and fireplace cement; heat, fire and acid resistant gaskets, pipe and
ceiling insulation (mostly amosite), fireproof drywall, flooring, lawn furniture,
roofing shingles, floor tiles, paper and cement products to provide heat
insulation due to its fire resistance qualities; coatings and friction products
such as for automobile clutches, brake and transmission parts. In the textile
industry asbestos strands extracted from the rocks (mostly
chrysotile, due to its flexibility) were woven and spun much like cotton or
other fabrics. The list of where and in what asbestos has been
used is incredibly extensive. |
| |